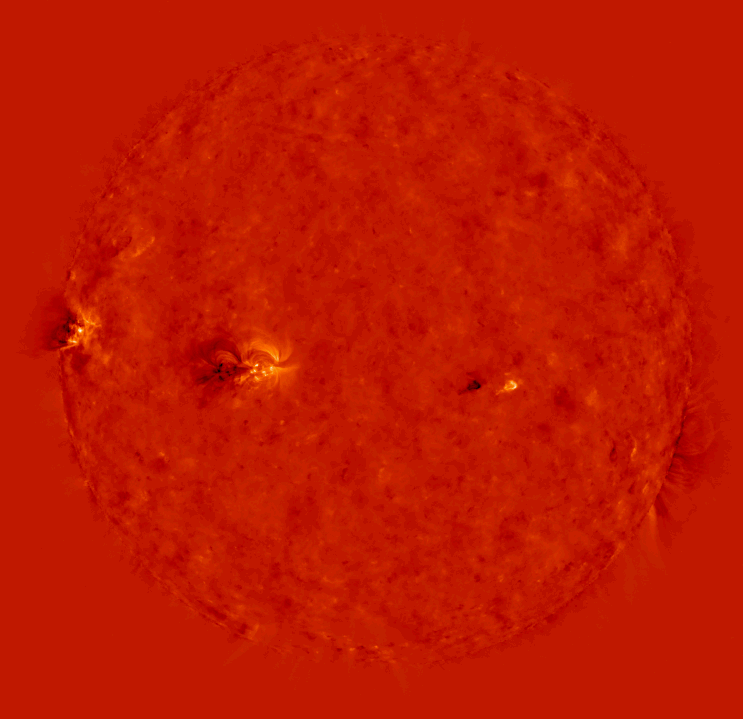
(a2) Coalignment of a Stereoscopic EUVI Image Pair
The coalignment between a stereoscopic image pair from spacecraft A and B
is accomplished by co-centering, rebinning, and rotating of image B to the
same parameters as image A, based on the information given in the FITS header
descriptors of the two images.

Let us coalign two EUVI images from spacecraft A and B on May 9, 2007,
20:40 UT, in the wavelength of 171 A. The IDL commands for this example:
IDL>
datadir='$secchi/lz/L0/'
;disk or data archive
date ='20070509'
;'YYYYMMDD' date of observation
tstart ='203500'
;'HHMMSS' start time interval for image selection
tend ='204500'
;'HHMMSS' end time interval for image selection
wave ='171'
;wavelength '171','195','284', or '304' (Angstroem)
color=0
;0=automated scaling of min/max, 1=interactive
movie=0
;0=automated movie play, 1=interactive stepping of images
euvi_files,datadir,date,tstart,tend,'a',wave,files_a
euvi_files,datadir,date,tstart,tend,'b',wave,files_b
euvi_display,files_a(0),color,movie,image_a,index_a
euvi_display,files_b(0),color,movie,image_b,index_b
euvi_stereopair,files_a,files_b,index_a,index_b,image_pair,para
savefile='loop_A.sav'
;data save file
save,filename=savefile,image_pair,para
;save data
The output is a pair of coaligned images according to the parameters of
image A, stored in the array IMAGE_PAIR. If the file lists FILES_A and
FILES_B contain multiple images, they are stacked together to a single
(averaged) A image and (averaged) B image in the pair IMAGE_PAIR(2,NX,NY).
Some important parameters used in
the following are stored in the structure PARA, containing information on
the common image size (NX,NY), the common Sun center position (CRPIX1,CRPIX2),
the distances of the spacecraft to the Sun (DA,DB), the solar radius in arcsec
(RSUN), the spacecraft separation angle (SEP_DEG), and the angle between the
spacecraft plane and the ecliptic plane (AB_DEG):
help,image_pair,para
IMAGE_PAIR INT = Array[2, 2048, 2048]
PARA STRUCT = -> Array[1]
help,para,/str

This is how the two images look before coalignment:
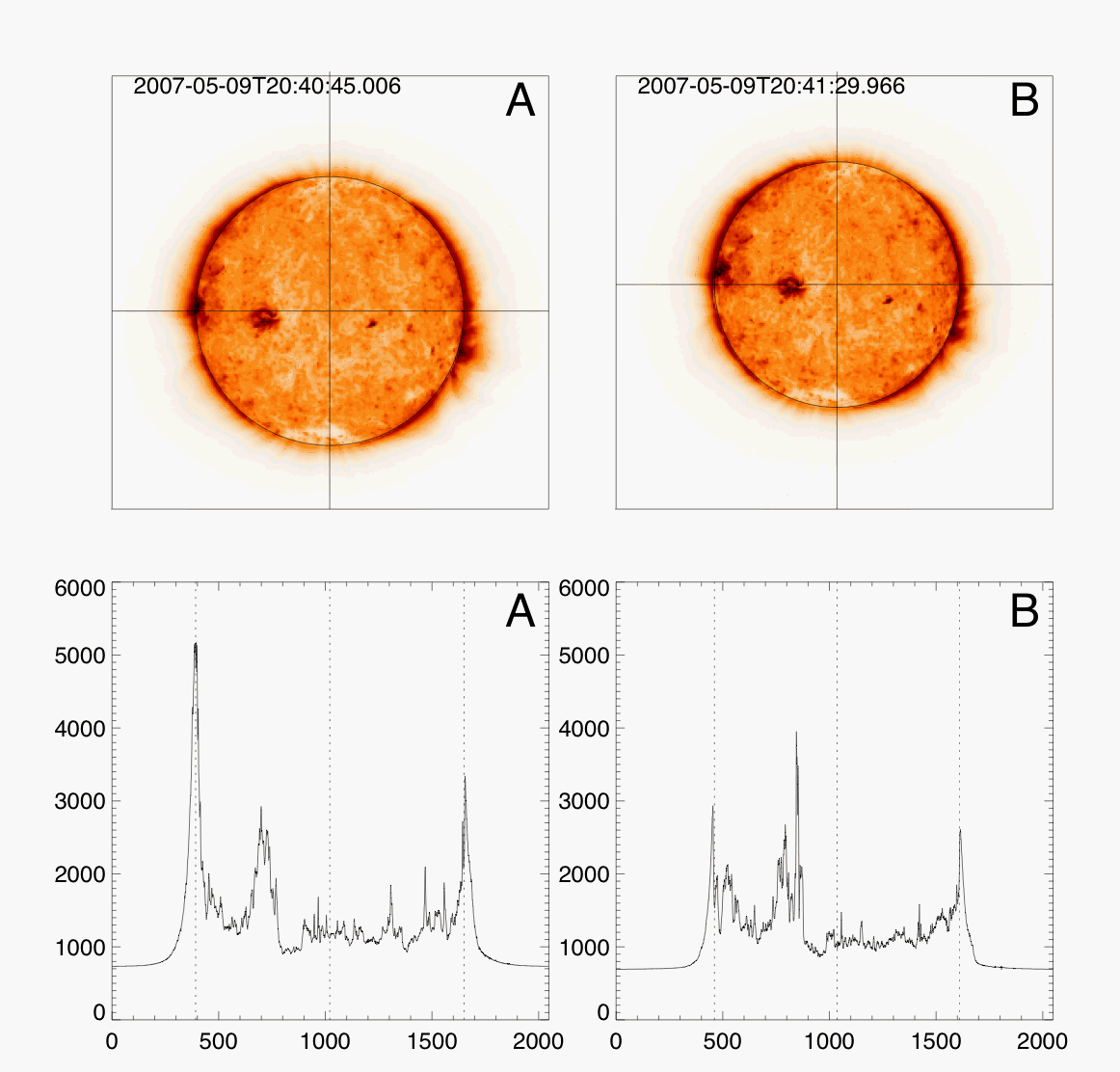
This is how the difference image looks after coalignment. A good test of
perfect coalignment is whether you see a mismatch of the limb around the Sun
in a difference image.